Exocrine glands
Epithelia in which
all the cells are specialized for secretion are usually
organized as the secretory portions of exocrine glands, which
are continuous with the epithelia of ducts through which the
secreted product is discharged.
Glands are
classified based on the structure of both the ducts and
secretory portions.
-
Ducts can be
branched (compound) or unbranched (simple)
-
The overall
shape of the glands’ secretory portions can be tubular,
acinar (rounded), or tubuloacinar (tubular with a rounded
end)
-
The secretory
portion may also be described further as branched tubular or
coiled tubular (i.e., long and not branched)
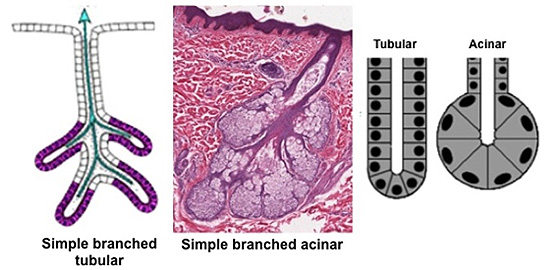
Study the following
examples of glands in some of these structural classifications.
Serous and
mucous elements of a gland. |