| Serous and mucous glands
Now let’s consider two main types of
secretory products produced by exocrine glands, serous and mucous
secretions.
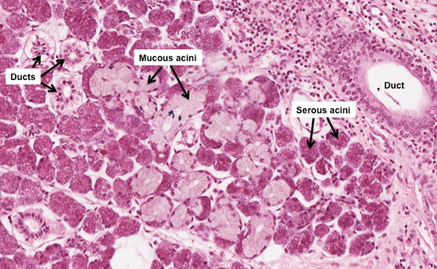
In these two slides of mixed
serous/mucous and purely serous salivary glands (submandibular gland
and parotid gland), respectively, note the staining differences that
result from the two different types of secretory products made by
these glands. These staining differences are important and reflect
fundamental differences in cell function.
- Serous acini secrete a
protein-rich product containing various digestive enzymes. These
secretory products stain well with eosin, giving the apical
cytoplasm where these secretory vesicles are stored an intense
pink color. Because these cells are producing a great deal of
secreted proteins, they will also exhibit basophilia in the
cytoplasm due to the presence of abundant rER.
- Mucous acini, like goblet
cells, secrete mucus, which is a watery, carbohydrate-rich
substance that is low in protein. Mucus-producing cells stain
very poorly because they contain little rER and their mucin
secretory granules react poorly with most stains, except PAS-Alcian
blue, which stains mucus purple.
So, how do the secretory cells actually
produce and release their product? |