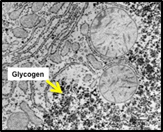
 Cytoplasmic
inclusions are primarily metabolic products that are stored in the
cytoplasm, typically in long-lived cells such as hepatocytes,
neurons, and cardiac muscle cells. Some examples of these include
glycogen granules (a storage form of glucose seen as small, dark
granules in the cytoplasm in TEM images), melanin pigment granules,
lipid droplets, and residual bodies or lipofuscin granules. Some of
these inclusions are visible in routinely prepared, H&E stained
sections, and most are visible in electron micrographs. Cytoplasmic
inclusions are primarily metabolic products that are stored in the
cytoplasm, typically in long-lived cells such as hepatocytes,
neurons, and cardiac muscle cells. Some examples of these include
glycogen granules (a storage form of glucose seen as small, dark
granules in the cytoplasm in TEM images), melanin pigment granules,
lipid droplets, and residual bodies or lipofuscin granules. Some of
these inclusions are visible in routinely prepared, H&E stained
sections, and most are visible in electron micrographs.
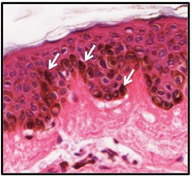 Melanin
pigment granules (arrows) are dark brown cytoplasmic inclusions that
are visible in H&E
stained specimens of skin.
They function to protect epithelial cells (keratinocytes) of the
epidermis from ultraviolet radiation. Melanin
pigment granules (arrows) are dark brown cytoplasmic inclusions that
are visible in H&E
stained specimens of skin.
They function to protect epithelial cells (keratinocytes) of the
epidermis from ultraviolet radiation.
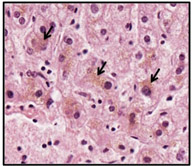 Residual
bodies or lipofuscin granules are another type of cytoplasmic
inclusions. These granules represent materials remaining after lysosomal degradation. In routinely prepared, H&E stained
specimens
of liver, lipofuscin may be visible as light brown granules in the cytoplasm
of hepatocytes. Residual
bodies or lipofuscin granules are another type of cytoplasmic
inclusions. These granules represent materials remaining after lysosomal degradation. In routinely prepared, H&E stained
specimens
of liver, lipofuscin may be visible as light brown granules in the cytoplasm
of hepatocytes.
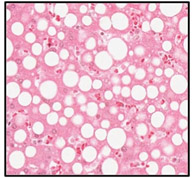 Lastly,
take a look at this specimen of a
fatty liver,
where lipid droplets are easily visualized as clear, circular spaces
in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes. Remember that lipids are extracted
during specimen preparation, resulting in empty spaces where lipid
droplets were present. Lastly,
take a look at this specimen of a
fatty liver,
where lipid droplets are easily visualized as clear, circular spaces
in the cytoplasm of hepatocytes. Remember that lipids are extracted
during specimen preparation, resulting in empty spaces where lipid
droplets were present.
Cytoskeletal
structure
comes next. |