|
Peripheral nerves usually
contain axons from motor, sensory, and autonomic neurons that are
mixed in bundles and organized into fascicles by connective tissue
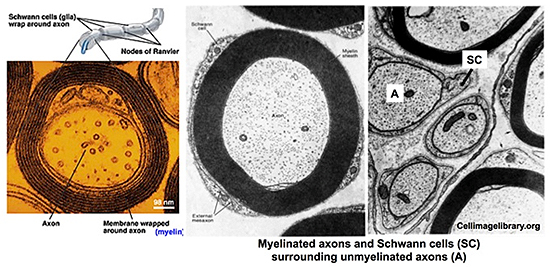
coverings. Schwann cells are the major glial cells of
peripheral nerves. They surround and support unmyelinated nerve
fibers (axons) and produce myelin sheaths that surround myelinated
nerve fibers. Review the structure of myelin in the figure below and
study the TEM images showing Schwann cells surrounding myelinated
and unmyelinated axons. Osmium used in preparation of these
specimens for TEM preserves the lipids of the myelin and stains them
black, making it easy to see the many concentric layers of the
sheath.
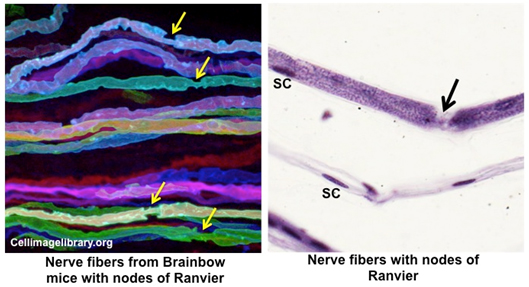
 Gaps in the
myelin sheaths between adjacent Schwann cells are called nodes of
Ranvier. These nodes allow for saltatory conduction where
nerve impulses or action potentials are able to rapidly move along
the axon by jumping from node to node. Examine the images below and
this preparation of isolated,
teased-apart nerve fibers. Identify
Schwann cell nuclei (SC) and nodes of Ranvier (arrows).
Next is more
about peripheral nerves. |