|
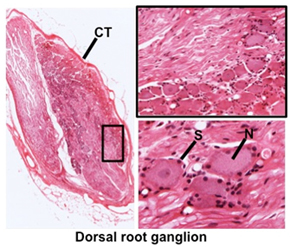 Ganglia are collections of
cell bodies outside the CNS for sensory or autonomic nerves. Outside
of the spinal cord Ganglia are collections of
cell bodies outside the CNS for sensory or autonomic nerves. Outside
of the spinal cord (this slide is from
thoracic level 6) or
on this
slide, locate
and examine a spinal or dorsal root ganglion. Identify: (this slide is from
thoracic level 6) or
on this
slide, locate
and examine a spinal or dorsal root ganglion. Identify:
- Large sensory neurons (N)
- Satellite cells
(S, glial cells) surrounding each neuron
- Connective tissue (CT)
covering the entire ganglion
Examine a
sympathetic ganglion
on this slide, and
identify the same structures just found in the sensory
ganglion.
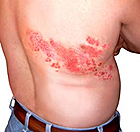 Clinical note: The herpes zoster virus, acquired during
childhood chicken pox, can remain dormant in neurons of sensory
ganglia. The virus can be reactivated in older individuals,
migrating along axons to the skin and producing blisters and a
painful rash known as shingles. Although skin symptoms usually heal
within weeks, the pain (post-herpetic neuralgia) may persist for
many months. Clinical note: The herpes zoster virus, acquired during
childhood chicken pox, can remain dormant in neurons of sensory
ganglia. The virus can be reactivated in older individuals,
migrating along axons to the skin and producing blisters and a
painful rash known as shingles. Although skin symptoms usually heal
within weeks, the pain (post-herpetic neuralgia) may persist for
many months.
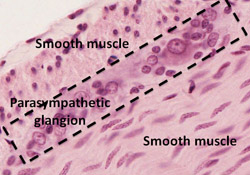 Smaller parasympathetic ganglia are found in the walls
of organs in the digestive tract where they function to regulate
contraction of smooth muscle. Examine the image at the right and
these slides of esophagus and
intestine)
to locate parasympathetic ganglia with their large neuronal cell
bodies surrounded by satellite cells. Smaller parasympathetic ganglia are found in the walls
of organs in the digestive tract where they function to regulate
contraction of smooth muscle. Examine the image at the right and
these slides of esophagus and
intestine)
to locate parasympathetic ganglia with their large neuronal cell
bodies surrounded by satellite cells.
Now let's look at
peripheral nerves. |