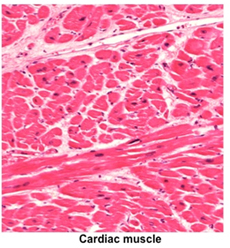
 Cardiac Muscle Cardiac Muscle
The myocardium of the heart wall is
composed of cardiac muscle fibers arranged as interwoven, spiral
layers aligned with the long axis of the heart ventricles. Cardiac
muscle fibers are striated like skeletal muscle fibers, and the
contraction cycle is similar to that of skeletal muscle. There are
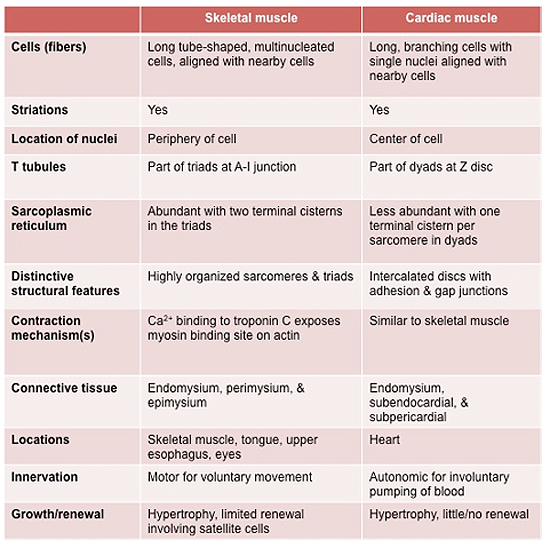
some key structural differences that distinguish cardiac and
skeletal muscle fibers. Review the table below highlighting these
differences.
Examine cardiac
muscle in the heart myocardium (sample
1 , sample 2), and
sample 3.
Identify fascicles, connective tissue layers, blood vessels, and
fibers cut in multiple planes. Identify intercalated discs and
distinguish these from striations. , sample 2), and
sample 3.
Identify fascicles, connective tissue layers, blood vessels, and
fibers cut in multiple planes. Identify intercalated discs and
distinguish these from striations.
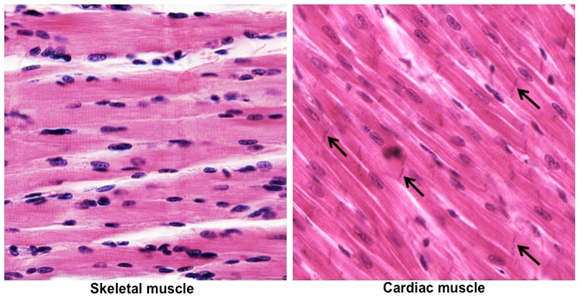
On the slides and in the images
below, compare cardiac and skeletal muscle. Note the similarities
(striations) and differences (branching fibers, centrally located
single nuclei, and intercalated discs) between these two types of
striated muscle.
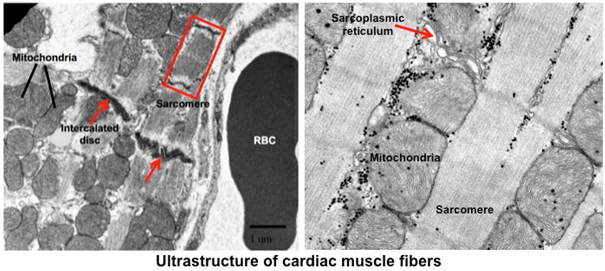
 Next, examine the ultrastructural features of
cardiac muscle cells in the images below. The structure of the
cardiac muscle sarcomere is the same as the skeletal muscle
sarcomere. However, the T tubule system and terminal cisternae of
the sarcoplasmic reticulum are organized as dyads, rather than the
triads that occur in skeletal muscle. Cardiac muscle cells also have
prominent step-like junctional complexes, intercalated discs,
containing adhesion and gap junctions that are important for
coordinating contraction of the cardiac muscle fibers.
Clinical note:
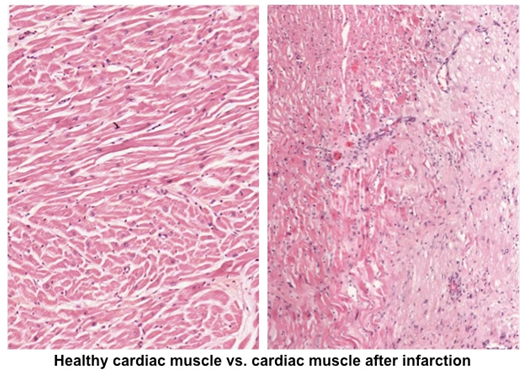
The fact that cardiac muscle lacks satellite cells severely limits
its capacity for repair after injury, such as injury from transient
ischemia during myocardial infarction (heart attack). As shown
below, injured cardiac muscle fibers degenerate and are replaced by
connective tissue. Cardiac muscle injury and degeneration causes
release of various cytoplasmic enzymes, which can be detected in the
circulating blood and used as an indicator of heart damage.
 Next is
smooth muscle. |