|
Muscle Contraction
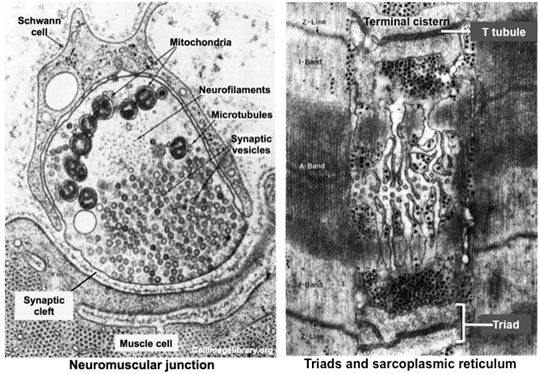
The neuromuscular junction or
motor end plate is the site where motor neurons form synapses
with skeletal muscle fibers. It is here where action potentials
traveling along the motor neuron trigger the events leading to
muscle contraction. Study the images below and
this slide to see
the association of motor neurons with skeletal muscle fibers.

Arrival of an action potential at the
axon terminus triggers the release of acetylcholine from synaptic
vesicles into the synaptic cleft. Acetylcholine binds acetylcholine
receptors on the muscle fiber sarcolemma, triggering its
depolarization. This depolarization travels along the T tubules,
resulting in release of Ca2+ from the terminal cisternae of the
sarcoplasmic reticulum into the sarcoplasm. Ca2+ binds troponin C,
unmasking the myosin-binding site on the actin thin filaments to
initiate the contraction cycle.
Study the electron micrographs below
showing the ultrastructural features of the neuromuscular junction
and the muscle fiber with its triads containing the T tubules and
terminal cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in close
association with the sarcomere. Recognizing the ultrastructural
features of the neuromuscular junction and skeletal muscle fibers
will help you understand the events involved in muscle contraction.
Moving right along to
cardiac muscle. |