|
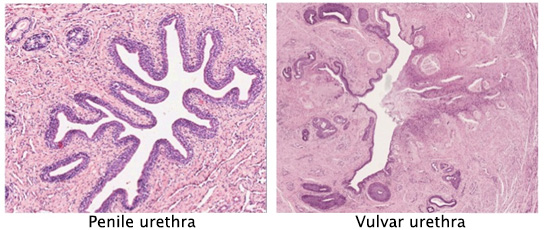
The urethra is a fibromuscular tube, which functions as a conduit for urine to exit the body. The penile urethra also serves as a conduit for semen during sexual function. The penile urethra has three segments, the prostatic, membranous, and penile or spongy urethra. It is lined by epithelia of different types, usually pseudostratified or stratified columnar that transitions to stratified squamous epithelium. The vulvar urethra is shorter and is initially lined by transitional epithelium that transitions to stratified squamous epithelium. Small urethral glands are located in the connective tissue underlying the epithelium and layers of striated muscle form the external voluntary urethral sphincter.
Examine the penile urethra in a transverse section of the penis and this specimen of vulvar urethra. Note the stratified squamous epithelium, associated urethral glands, and muscle layers.
Now try this self-assessment
quiz, no one sees the score but you.
The Gonadal System is the next unit. |