|
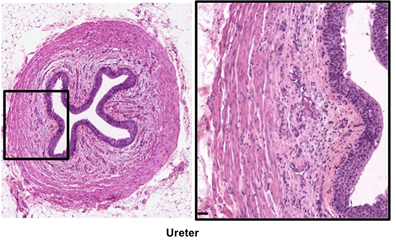
 The ureters are tubes
continuous with the renal pelvis, which transport urine from the
kidneys by peristalsis. The ureters are tubes
continuous with the renal pelvis, which transport urine from the
kidneys by peristalsis.
- Examine images below and these
slides of ureter (sample
1, sample 2),
noting the folded mucosa surrounded by two layers of smooth
muscle and adventitia. In the folds of the urinary epithelium
(or urothelium) note the umbrella shaped surface cells and the
thin basement membrane with closely associated capillaries.
The bladder collects urine from the ureters for storage and drainage
via the urethra.
-
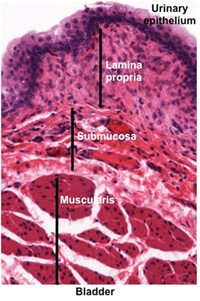
Examine the image below and
trichrome-stained and an
H&E
stained sections
of bladder. Observe the urinary or transitional epithelium that
is specialized to withstand the hypertonic urine and to distend
when the bladder is full. Identify the lamina propria, submucosa,
muscularis with three layers of smooth muscle (detrusor muscle),
and outer serosa/adventitia. The outer layer may contain Pacinian corpuscles, which sense pressure within the
bladder.
Clinical note: Transitional cell carcinoma, the most
common type of bladder cancer, is associated with occupational
exposure to certain organic chemicals among workers in the dye,
rubber, paint, and some other industries. Smokers also have a
four-fold increased risk for bladder cancer compared to
nonsmokers.
Almost there, last comes
the urethra. |