The Heart
- Next, examine this
specimen of
heart and
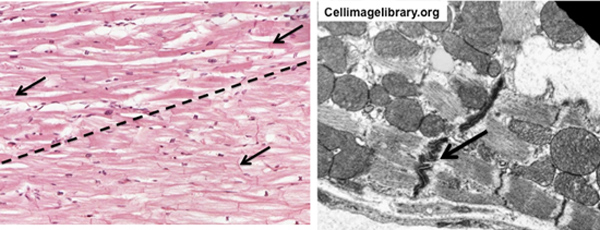
the image below on the left. Compare the appearance of the
cardiac muscle fibers (top half of image) and Purkinje fibers
(lower half of image). They both contain intercalated discs, but
the Purkinje fibers are larger and have paler staining cytoplasm
due to the presence of abundant glycogen and fewer myofibrils.
Intercalated discs are specialized intercellular junctions that
provide adhesion and communication, allowing the muscle cells to
coordinate their contraction.
- Finally, let’s consider the valves.
Heart valves must be shaped so that their leaflets fit precisely
together in order to prevent backflow or regurgitation of blood.
They must also open freely and completely so as not to restrict
blood leaving the chamber. If abnormal or misshapen due to infection
or congenital malformation, regurgitation of blood back through the
valve will occur and is detectable as a murmur.
- Heart valves are
anchored to the fibrous cardiac skeleton and chordae tendinae. They
are lined by endothelium and have a core of dense connective tissue
with elastic fibers. Examine the histology of a
heart valve in this trichrome stained
slide of heart.
The elastic and
large arteries comes next. |