|
The spleen is the largest lymphoid
organ in the body. It is the only lymphoid organ that filters the
blood, allowing for B and T cells to be activated in response to
antigens in the blood. The spleen also contains abundant macrophages
that function to remove old red blood cells from the circulation and
destroy them.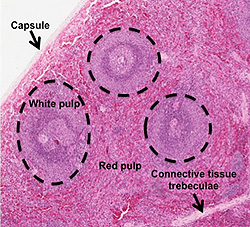
- Examine this section of
spleen
 and the
image at the right, and identify the capsule, connective
tissue trabeculae, and the overall organization of the
spleen into white pulp and red pulp. and the
image at the right, and identify the capsule, connective
tissue trabeculae, and the overall organization of the
spleen into white pulp and red pulp.
-
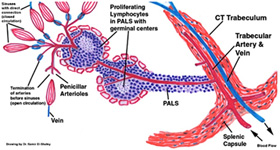 The arterial supply to the
white and red pulp is shown in the diagram at the right.
The
components are difficult to observe in routine histological
preparations, but you should understand the blood flow and try to
identify the major structures on your slide. Click the image for
the expanded view. The arterial supply to the
white and red pulp is shown in the diagram at the right.
The
components are difficult to observe in routine histological
preparations, but you should understand the blood flow and try to
identify the major structures on your slide. Click the image for
the expanded view.
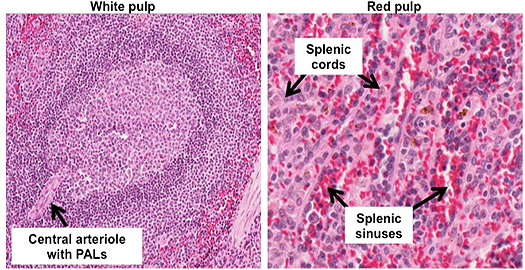
- On the slide and image below,
identify central arterioles associated with the white pulp
lymphoid follicles, the T cell-rich periarteriolar lymphoid
sheathes (PALS), as well as the marginal zone of these
follicles. Try to find a vascular sinus showing the unusual
nature of the lining endothelial cells or stave cells.
- In the red pulp, identify the
splenic cords (of Billroth), seen in the lower right image, and
the venous sinuses. The latter are small in this
section of spleen,
but can be detected by their contents of red blood cells.
Sheathed vessels and sinuses are seen more readily in
this section of spleen,
which is stained with a special stain that also demonstrates
elastic fibers in the trabeculae.
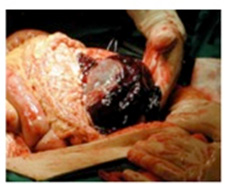
Clinical note: Because its capsule is
thin and the blood-filled red pulp is very delicate, the spleen is
easily ruptured by injury to the abdomen. This is a very serious
event that can lead to death from the loss of blood into the
abdominal cavity. Pictured to the right is a fatal splenic rupture.
Now try this
try this
short quiz to practice what you've learned.
Next is the
digestive system. |