|
 Lymph nodes are small,
bean-shaped organs that possess afferent and efferent lymphatic
vessels, allowing them to function as in-line filters for lymph that
drain from tissues and organs throughout the body. Lymph nodes
filter lymph and provide a site for presentation of antigens that
are carried in the lymph to B and T cells, promoting their
activation and mounting an immune response to foreign substances,
cells, and microorganisms. (Click here for a
larger image of the
lymph node.) Lymph nodes are small,
bean-shaped organs that possess afferent and efferent lymphatic
vessels, allowing them to function as in-line filters for lymph that
drain from tissues and organs throughout the body. Lymph nodes
filter lymph and provide a site for presentation of antigens that
are carried in the lymph to B and T cells, promoting their
activation and mounting an immune response to foreign substances,
cells, and microorganisms. (Click here for a
larger image of the
lymph node.)
Examine sections of lymph nodes (sample
1 , sample 2) and
images below. First, note the overall organization of the lymph
nodes (cortex containing lymphatic nodules, paracortex, and
medulla). , sample 2) and
images below. First, note the overall organization of the lymph
nodes (cortex containing lymphatic nodules, paracortex, and
medulla).
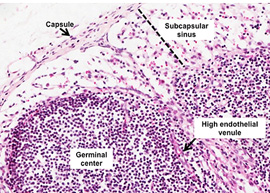 At higher
magnification, examine these structures: subcapsular sinus, lymphoid
follicles (also called lymphatic nodules), high endothelial venules,
and medullary cords and sinuses. As you find these structures,
consider the path of lymph flow. Lymph enters the lymph node through
afferent lymphatic vessels that pass through the capsule, it then
flows into the subcapsular sinus, along the cortical or trabecular
sinuses, into the medullary sinuses, and out through the efferent
lymphatic vessels. As lymph flows through the node it brings
antigens in close contact with B and T cells and antigen-presenting
cells in the lymphatic nodules and medullary cords. (Click here for
a
larger image of lymph node detail
to the right. Click here for
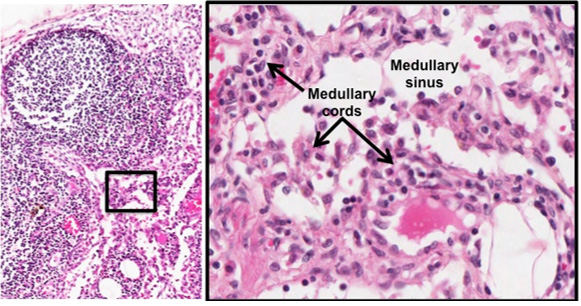
printable version of image below.) At higher
magnification, examine these structures: subcapsular sinus, lymphoid
follicles (also called lymphatic nodules), high endothelial venules,
and medullary cords and sinuses. As you find these structures,
consider the path of lymph flow. Lymph enters the lymph node through
afferent lymphatic vessels that pass through the capsule, it then
flows into the subcapsular sinus, along the cortical or trabecular
sinuses, into the medullary sinuses, and out through the efferent
lymphatic vessels. As lymph flows through the node it brings
antigens in close contact with B and T cells and antigen-presenting
cells in the lymphatic nodules and medullary cords. (Click here for
a
larger image of lymph node detail
to the right. Click here for
printable version of image below.)
Finally, take a look at
this silver
stained slide of
lymph node to see the reticular connective tissue that supports the
lymphocytes and other immune cells within the lymph nodes.
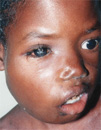 Clinical
note: Lymphomas involve neoplastic growth of lymphocytes,
commonly within lymph nodes. There are several types, depending on
the type of lymphocyte and the stage of differentiation involved. In
the early stage, lymphomas commonly involve cell accumulation caused
by their failure to undergo apoptosis. Pictured here is a child with
Burkitt's lymphoma. Clinical
note: Lymphomas involve neoplastic growth of lymphocytes,
commonly within lymph nodes. There are several types, depending on
the type of lymphocyte and the stage of differentiation involved. In
the early stage, lymphomas commonly involve cell accumulation caused
by their failure to undergo apoptosis. Pictured here is a child with
Burkitt's lymphoma.
Now for specifics on the tonsils. |