|
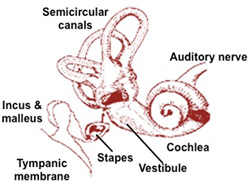 The ear contains structures
that provide the senses of hearing and equilibrium. It is divided
into three compartments: the external (receives sound waves), middle
(converts sound waves into mechanical waves and transmits them to
the fluid of the inner ear), and inner ear (converts mechanical
movements within fluid into nerve impulses to provide hearing and
equilibrium). Review the general organization and functions of the
middle and inner ear in the diagram and table below. The ear contains structures
that provide the senses of hearing and equilibrium. It is divided
into three compartments: the external (receives sound waves), middle
(converts sound waves into mechanical waves and transmits them to
the fluid of the inner ear), and inner ear (converts mechanical
movements within fluid into nerve impulses to provide hearing and
equilibrium). Review the general organization and functions of the
middle and inner ear in the diagram and table below.
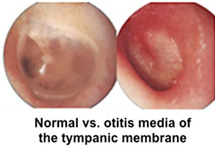 Clinical note: Bacterial
infections of the middle ear cavity (otitis media) are common
complications of colds and upper respiratory tract infections in
small children. If such an infection does not respond to
antibiotics, the resulting fluid and inflammatory material may be
drained through a perforation in the tympanic membrane. In the image
to the right the ear drum on the left is healthy, whereas the one on
the right is markedly inflamed and must have hurt. Clinical note: Bacterial
infections of the middle ear cavity (otitis media) are common
complications of colds and upper respiratory tract infections in
small children. If such an infection does not respond to
antibiotics, the resulting fluid and inflammatory material may be
drained through a perforation in the tympanic membrane. In the image
to the right the ear drum on the left is healthy, whereas the one on
the right is markedly inflamed and must have hurt.
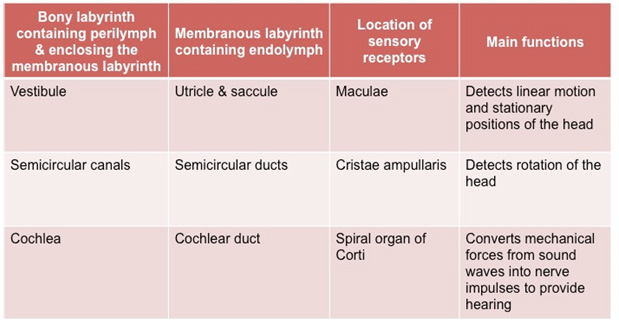
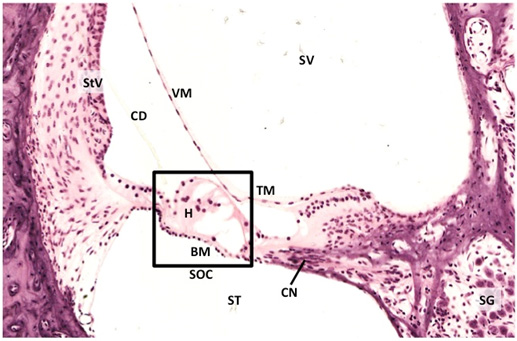
The cochlea is a spiral shaped,
bony organ enclosing a membranous region, the cochlear duct.
The bony labyrinth (including the scala vestibuli and
scala tympani) contains perilymph, whereas the membranous
labyrinth (scala media) contains endolymph. The cochlear duct houses
the spiral organ of Corti, the structure containing hair
cells with an underlying basilar membrane and overlying
tectorial membrane. Pressure waves moving through the
perilymph and endolymph displace these membranes, bending the
stereocilia on the hair cells and producing nerve impulses that
provide hearing.
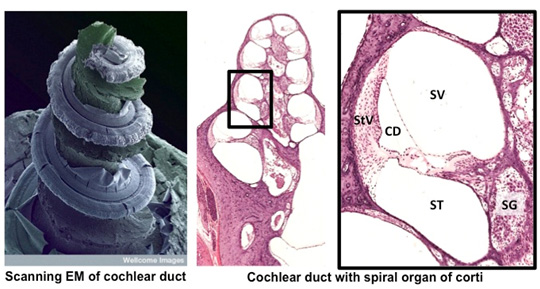
Examine the images below and this
section of the inner ear. This specimen
was dissected from the skull and sectioned to best demonstrate
structures within the conical, spiral-shaped cochlea. Identify the following:
- Spiral ganglion (SG) and cochlear nerve (CN)
- Spiral organ
of Corti (SOC)
- Ducts associated with the organ of Corti (scala
vestibule SV, scala media SM, scala tympani ST)
- Vestibular membrane (VM)
- Tectorial
and basilar membranes (TM, BM)
- Stria vascularis (StV)
- Hair cells (H)
 Clinical note:
Degeneration of hair cells in the organ of Corti is a common
cause of hearing loss in older individuals. Recent research has
shown the ability of hair cells to regenerate in certain
experimental systems and this is now an important area of
research in sensory neuroscience. Click the image for an
expanded view.
Watch this YouTube movie, one of the
best we've seen, detailing auditory transduction (how we hear). Because it's YouTube,
there will be a short commercial message, which within a few minutes you
can skip.
Now for the
vestibular structures. |