|
The eyes are photosensitive organs
that provide for the sense of sight by collecting and analyzing the
shape, intensity, and color of light reflected from objects. Light
enters the eye through the transparent cornea, passing through the
anterior chamber and pupil, and through the lens and vitreous before
striking the retina. Review the histological features and functions
of the eye structures in the table below.
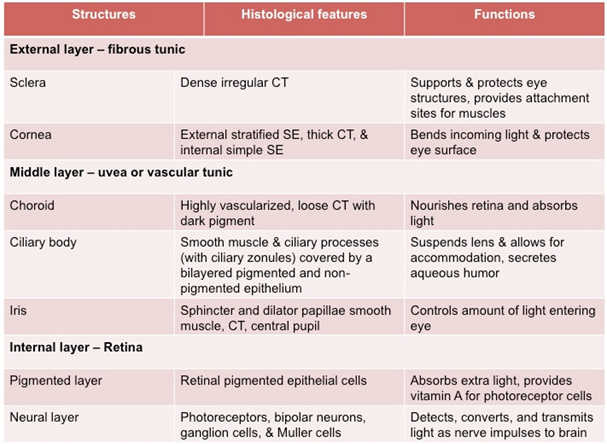
Examine the diagram and image below and
these two sections of the eye (sample
1 and sample 2) at
low power. From anterior to posterior, identify: cornea, iris,
lens, ciliary body, location of the vitreous (vitreous is
extracted during tissue processing), retina, and optic
nerve.
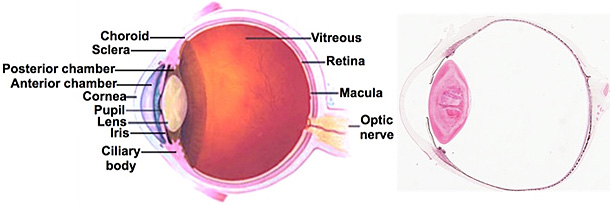
In the images at the right and
sample 1, carefully
examine the retina. Identify the retinal pigmented
epithelial cells (RPE), the rods and cones
(R&C, photoreceptor cells), the three layers of cell bodies (ganglionic
layer GL, inner nuclear layer INL, and outer nuclear layer
ONL), the inner and outer plexiform layers (IPL and OPL),
outer limiting layer (OLL), inner limiting membrane (ILM), choroid
(C) with capillaries, and sclera (S).
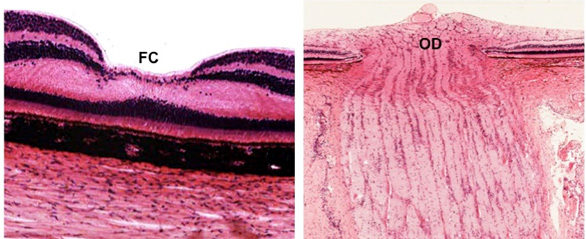
Identify the
fovea centralis (FC) and optic disc (OD) (where the optic
nerve meets incoming axons from the retina) as seen in the images
below.
More about the
eye. |