|
The fibers of Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is largely composed
of extracellular matrix. Extracellular matrix is composed of
fibrillar components and ground substance. The main fibers are
elastic and collagens. Eosin effectively stains type I collagen and
this accounts for the bundle staining observed in most H&E sections.
However, fibrillar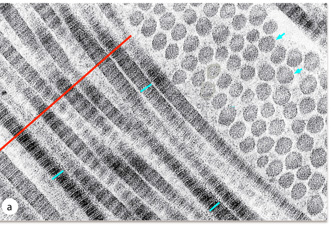 collagens have a unique structure that can be
observed in the EM. collagens have a unique structure that can be
observed in the EM.
Fibrillar collagens
The high magnification TEM shows
collagen. The short blue lines indicate collagen fibrils cut
longitudinally showing the alternating light and dark regions,
representing the overlap and gap regions respectively. The blue
arrows are at cross sections of fibrils, and the individual dots
within the circle are individual triple helices. The red line
indicates a grouping of fibrils called a fiber. (Image from
Junqueira’s Basic Histology 14th edition)
Elastic Fibers
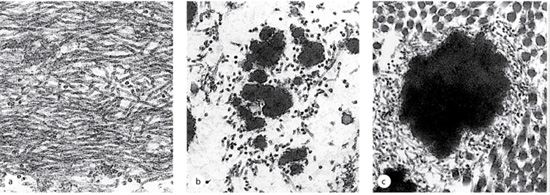
The series of TEMs illustrate elastic
fiber assembly. a) Shows the microfibers (fibrillin) which are
secreted first by fibroblasts. Next, elastin (dark amorphous
material) is secreted and aggregates on the microfibrils (b). (c)
The mature elastic fiber has elastin aggregated in the middle and
microfibrils surrounding it. (Image Junqueira’s Basic Histology 14th
edition)
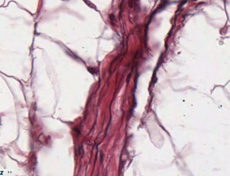 Elastic
fibers have a high concentration of glycosylated amino acid residues
and generally don't stain well with H&E in the light microscope.
Typically elastic fibers are visualized with specialized stains such
as aldehyde fuchsin. Now look for elastic fibers in the tunica media
(middle layer) of these two slides (sample
1, sample 2). On
the connective tissue slide showing small arteries and vein, examine
the internal and external
elastic laminae on either side of the tunica media. Elastic
fibers have a high concentration of glycosylated amino acid residues
and generally don't stain well with H&E in the light microscope.
Typically elastic fibers are visualized with specialized stains such
as aldehyde fuchsin. Now look for elastic fibers in the tunica media
(middle layer) of these two slides (sample
1, sample 2). On
the connective tissue slide showing small arteries and vein, examine
the internal and external
elastic laminae on either side of the tunica media.
Try this sample self-assessment
quiz.
Next is nervous
tissue. |