Dense Connective Tissue Proper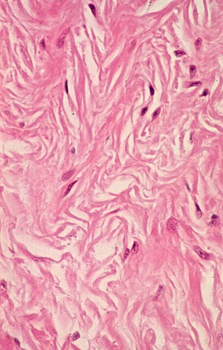
Dense CT is characterized by abundant collagen fibers arranged in
large bundles, with a predominance of type I collagen. You’ll find
relatively fewer cells and less ground substance in these specimens.
Dense CT can be described further as “irregular” (DICT) or “regular”
(DRCT), depending on fiber arrangement.
Dense irregular CT
Dense irregular CT consists of collagen fibers arranged in bundles
that are oriented in various directions; this arrangement provides
significant strength to resist stress and shearing forces in
multiple directions. You will find it in the submucosa of
gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts, the reticular dermis of
skin, and the outer surface or “capsule” of some organs (don’t worry
at this point about terminology related to specific anatomical areas
– it will be described in later modules). The stroma or packaging
material around secretory units and supporting epithelia also
usually contain dense irregular CT.
Identify dense irregular CT in slides
of adrenal gland,
testis and
bone
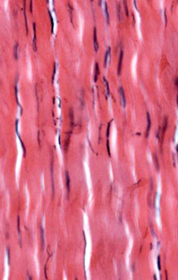
Dense regular CT
In contrast to dense irregular CT, dense regular CT consists of
ordered arrays of collagen fibers (mostly type I) and very little
ground substance. Specialized fibroblasts (tendinocytes) are
typically seen aligned with the orientation of the fibers. The
parallel arrangement and dense packing of fibers provide maximum
strength for structures such as tendons, ligaments, and aponeuroses.
- Identify this tissue type in
slides of tendon:
longitudinal section and
cross section.
- Examine the more active
fibroblasts in this region, noting their characteristic features
- Note the regular parallel
arrangement of the collagen fibers and relative absence of other
cells besides fibroblasts
- The relatively low density of cells
and blood vessels among the collagen bundles in tendon helps
increase the tensile strength of this tissue but also contributes to
its extremely slow rate of healing after injury.
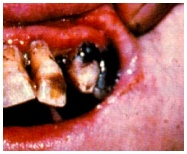
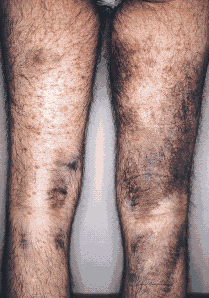
Clinical note: Without an
adequate supply of vitamin C, as in the nutritional deficiency
scurvy, collagen I and II do not polymerize properly, leading to the
following signs
- Slow wound healing
- Distension of blood vessels
- Ease of bruising
- Loosening of
the teeth and bleeding gums
Now, let’s review various
types of specialized CT. |
 |
 |
|