|
The penis contains the
urethra, which serves as a conduit for urine and semen, and
three bodies of erectile tissue that produce erection when their
abundant vascular sinuses fill with blood. The urethra is lined by
pseudostratified columnar epithelium that transitions to stratified
squamous epithelium. Small urethral glands are present in the lamina
propria whose secretions function to lubricate the urethra.
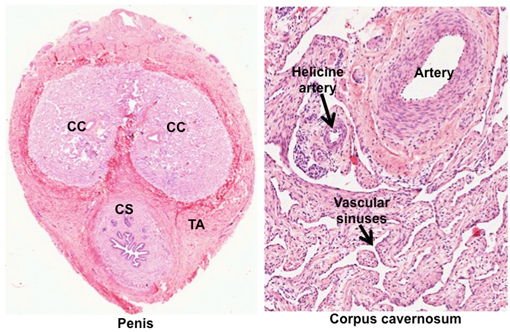
- Examine the images below and a
section of the penis, and identify
the two corpora cavernosa (CC) and the
corpus spongiosum (CS) surrounding the urethra. These three
bodies are cylinders of erectile, cavernous tissue. Within them
identify the helicine arteries and the large vascular
sinuses in the connective tissue surrounding the arteries.
Fibroelastic connective tissue, the tunica albuginea (TA),
surrounds the three corpora.
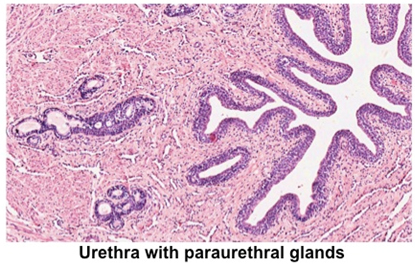
- Next, identify the folded mucosa
of the urethra. Near the urethra, note the small paraurethral
glands that secrete mucus.
 Clinical
note: The drug Viagra treats impotence or erectile dysfunction
by targeting the population of smooth muscle cells in the
microvasculature of the corpora cavernosa. Increasing the
contractility of these cells facilitates the events that lead to the
cavernous tissue filling with blood. Clinical
note: The drug Viagra treats impotence or erectile dysfunction
by targeting the population of smooth muscle cells in the
microvasculature of the corpora cavernosa. Increasing the
contractility of these cells facilitates the events that lead to the
cavernous tissue filling with blood.
Try this self-assessment
quiz to practice what you have learned.
Now for the
Endocrine System. |