|
The thyroid gland produces,
stores, and secretes thyroid hormone that increases the body’s basal
metabolic rate and calcitonin that reduces blood calcium levels. The
thyroid is a unique gland because it partially synthesizes and
stores its hormone product in the lumens of the thyroid follicles.
The thyroid follicles are lined by a simple cuboidal epithelium
containing thyrocytes (follicular cells or principle cells,
produce thyroid hormone) and parafollicular cells (produce
calcitonin). The follicle lumens are filled with an eosinophilic
material called colloid where thyroid hormone is synthesized and
stored.
- Examine the images below and
these two sections of thyroid (sample
1, sample 2
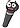 ).
The thyroid is surrounded by a thin connective tissue capsule
and is divided into irregular lobules by septa that extend from
the capsule. Identify thyroid follicles, colloid,
thyrocytes, and parafollicular cells. ).
The thyroid is surrounded by a thin connective tissue capsule
and is divided into irregular lobules by septa that extend from
the capsule. Identify thyroid follicles, colloid,
thyrocytes, and parafollicular cells.
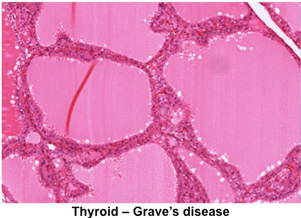
Clinical note: Increased
height of thyroid follicular cells and infoldings of the follicle
wall are indications of hyperthyroidism or Grave’s disease, a
disorder characterized by restlessness, sleeplessness, tremor, and
exophthalmos. Treatment is subtotal thyroidectomy or use of
radioactive iodine to destroy or inactivate the thyroid follicles.
Parathyroids
are next. |