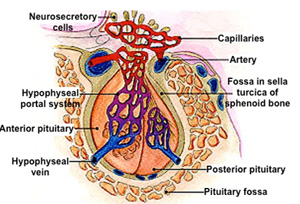
 The
pituitary gland (hypophysis) is considered to be a master gland because of the hormonal
control it exerts on many other glands. Study the diagram of the
pituitary gland noting the relationships between the anterior and
posterior lobes, the vascular supply, and the hypothalamus of the
brain. The hypothalamus-hypophyseal portal system has a
central role in pituitary function because it carries regulatory
hormones from the median eminence of the hypothalamus to the
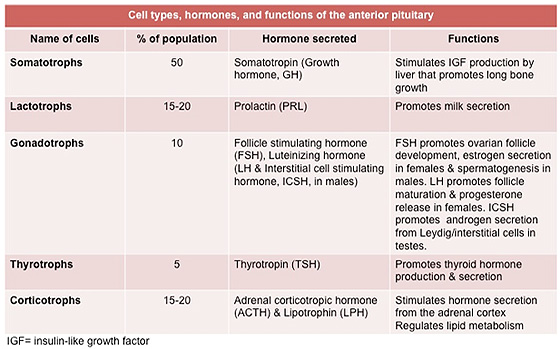
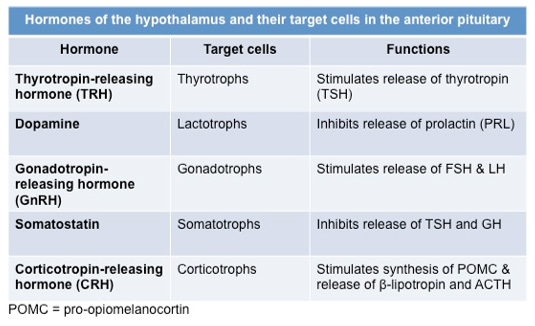
endocrine cells of the anterior pituitary. Review the tables below
summarizing the hormones of the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
and their actions. The
pituitary gland (hypophysis) is considered to be a master gland because of the hormonal
control it exerts on many other glands. Study the diagram of the
pituitary gland noting the relationships between the anterior and
posterior lobes, the vascular supply, and the hypothalamus of the
brain. The hypothalamus-hypophyseal portal system has a
central role in pituitary function because it carries regulatory
hormones from the median eminence of the hypothalamus to the
endocrine cells of the anterior pituitary. Review the tables below
summarizing the hormones of the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary
and their actions.
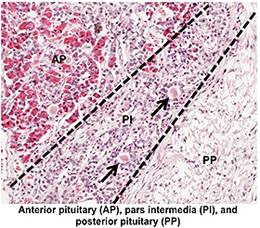
- Examine the image at the right and
these two sections of pituitary gland (sample 1
 ,
sample 2 ,
sample 2 ).
Identify the anterior pituitary, the posterior pituitary, and the
intervening pars intermedia with cysts (arrows) representing
remnants of Rathke's pouch. Note the abundance of large capillaries
among the clusters of glandular epithelial cells in the anterior
pituitary. The pars intermedia, as seen in
this specimen,
is poorly developed in humans. ).
Identify the anterior pituitary, the posterior pituitary, and the
intervening pars intermedia with cysts (arrows) representing
remnants of Rathke's pouch. Note the abundance of large capillaries
among the clusters of glandular epithelial cells in the anterior
pituitary. The pars intermedia, as seen in
this specimen,
is poorly developed in humans.
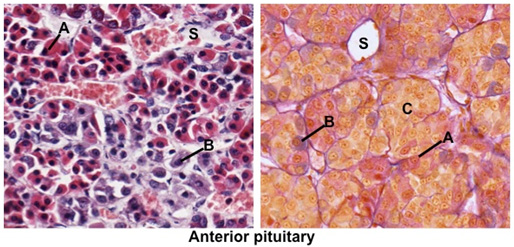
This
slide of pituitary shows a section of the gland prepared with a special trichrome stain
that demonstrates the different staining properties of the secretory
cells in the anterior pituitary. Identify acidophils (A), basophils
(B), chromophobes (C), and sinusoids (S) in this specimen and in the
images below.
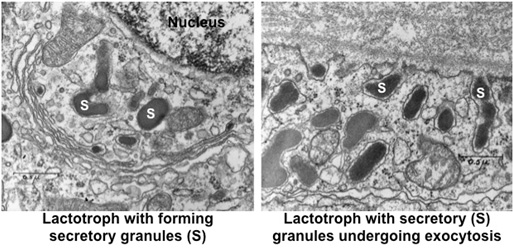
Finally, examine the ultrastructural features of the
endocrine cells in the anterior pituitary. The TEM images below show
lactotrophs forming and releasing their secretory granules
containing prolactin.
Posterior
pituitary is next. |