|
 The tongue is a muscular organ
that contains structures that assist in speech, positioning of food
in the oral cavity, providing the sensation of taste, digestion
(minor salivary glands), and immune response (lingual tonsil). The
dorsal surface of the tongue is lined by partially keratinized oral
mucosa containing numerous papillae (filiform, fungiform,
foliate, and circumvallate) that have mechanical and sensory
functions. The thick skeletal muscle of the tongue is arranged in
three planes, allowing for precise movements. The tongue is a muscular organ
that contains structures that assist in speech, positioning of food
in the oral cavity, providing the sensation of taste, digestion
(minor salivary glands), and immune response (lingual tonsil). The
dorsal surface of the tongue is lined by partially keratinized oral
mucosa containing numerous papillae (filiform, fungiform,
foliate, and circumvallate) that have mechanical and sensory
functions. The thick skeletal muscle of the tongue is arranged in
three planes, allowing for precise movements.
- Examine the images at the right
and sections of the tongue (sample
1, sample 2),
and identify filiform and fungiform papillae on
the dorsal surface.
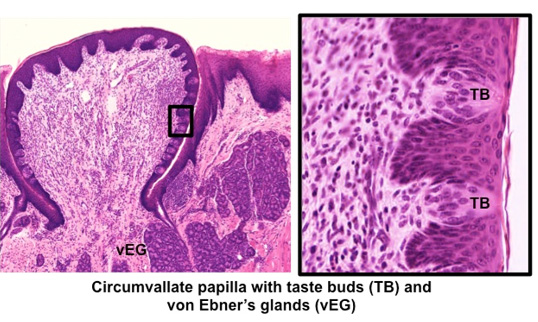
- In the images below and on this
section of tongue,
look for a circumvallate papilla. Identify taste buds on
the lateral surface and the serous von Ebner's glands
associated with circumvallate papillae.
 Let's take a look at the
salivary glands. |