|
The large Intestine is the
site for absorption of water and elimination of solid waste. It
contains the typical layers of the GI tract: mucosa, submucosa,
muscularis externa and adventitia/serosa. The large intestine mucosa
contains crypts, but no villi, and the lining epithelium is similar
to that of the small intestine, containing simple columnar
absorptive epithelial cells (colonocytes) and many goblet cells. The
three regions (cecum, colon, and rectum) of the large intestine are
similar histologically.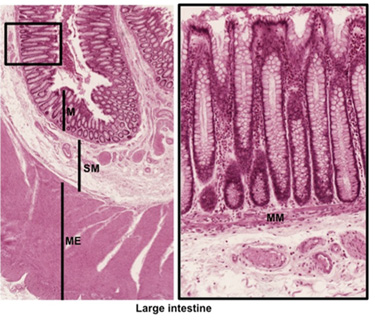
- Examine this
section of colon,
and identify the major layers and sublayers. Note that the
muscularis externa of the large intestine differs from that of
the small intestine because it contains an outside layer of
three longitudinally oriented bands of smooth muscle, the
teniae coli. Locate the myenteric plexi, which are distinct
on this slide.
The mucosa and submucosa are highly folded in
this specimen. The mucosa is invaginated into many straight,
tightly packed colonic glands, lined by columnar mucus-secreting
cells. In the lumen, note the solid waste and indigestible
material covered with mucus.
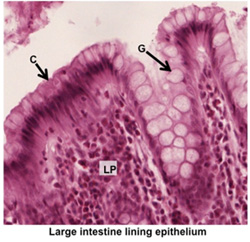
- Next, examine the images at the
right and these two slides of colon at higher magnification (sample
1, sample 2
 ).
Locate the simple tubular colonic glands cut transversely. Note
their small lumens, the lining epithelium containing
colonocytes (C) or columnar absorptive cells and
mucus-secreting goblet cells (G), and the many
lymphocytes and capillaries in the surrounding lamina propria
(LP). ).
Locate the simple tubular colonic glands cut transversely. Note
their small lumens, the lining epithelium containing
colonocytes (C) or columnar absorptive cells and
mucus-secreting goblet cells (G), and the many
lymphocytes and capillaries in the surrounding lamina propria
(LP).
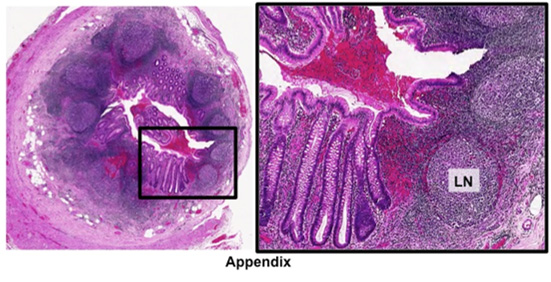
- Examine the appendix in the
images below and on these two slides (sample
1, sample 2)
Note that its histology is similar to the rest of the large
intestine, but that it contains abundant lymphatic nodules (LN).
- Finally, examine this specimen
of the anal
canal, noting its stratified squamous, keratinized
epithelium and the smooth muscle of the internal anal sphincter
and striated muscle of the external anal sphincter.
Now try this self-assessment
quiz, no one sees the score but you.
Now for liver, gallbladder and
pancreas. |