|
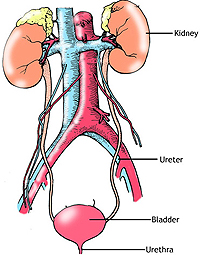 The
urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and
urethra and is responsible for the important bodily functions of
soluble waste production, storage, and elimination. Urine containing
waste substances is produced in the kidney as a blood filtrate. It
is transported via the ureters to the bladder where it is stored and
eventually eliminated through the urethra. This process also results
in the salvaging of water, sugars, proteins, and ions from the blood
filtrate, which are returned to the blood. The kidneys also have a
variety of other important functions. They play a role in
controlling systemic blood pressure by the secretion of renin,
erythrocyte production by secretion of erythropoietin, excretion of
drugs and other bioactive substances, and activation of vitamin D. The
urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and
urethra and is responsible for the important bodily functions of
soluble waste production, storage, and elimination. Urine containing
waste substances is produced in the kidney as a blood filtrate. It
is transported via the ureters to the bladder where it is stored and
eventually eliminated through the urethra. This process also results
in the salvaging of water, sugars, proteins, and ions from the blood
filtrate, which are returned to the blood. The kidneys also have a
variety of other important functions. They play a role in
controlling systemic blood pressure by the secretion of renin,
erythrocyte production by secretion of erythropoietin, excretion of
drugs and other bioactive substances, and activation of vitamin D.
The learning objectives for this unit
are:
- Identify the histologic and
cellular characteristics of the functional components of the
nephron and verify their relationships with either the kidney
cortex or medulla.
- Identify the structural and
cellular characteristics of the ureter, urinary bladder, and
urethra.
Let's start with the
basic
structure of the kidney. |