|
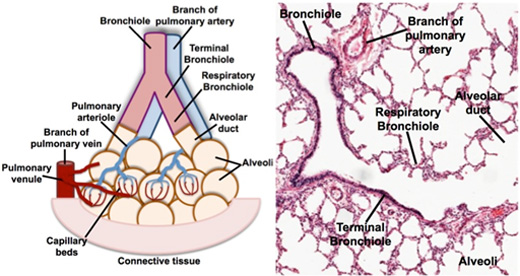
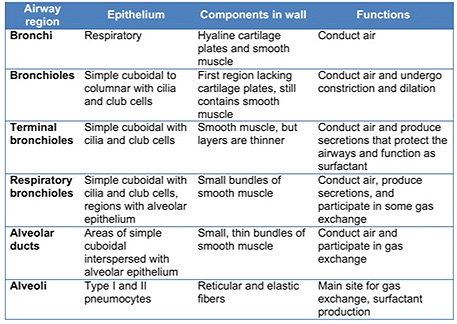
The lungs contain conducting
portions (bronchi that lead to terminal bronchioles) through which
air passes and respiratory portions (respiratory bronchioles that
lead to the alveoli) where gas exchange occurs. Study the functional
organization of lung tissue on the diagram and corresponding image,
noting how bronchioles branch into terminal bronchioles, which lead
into the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli. Also,
note the intrapulmonary blood circulation around the alveoli.
 Clinical
note: Asthma involves hyperirritability of the respiratory
passages, expressed as contraction of the bronchial smooth muscle,
edema of the mucosa, and increased mucus secretion. It may be
transient, following an upper respiratory tract infection, but more
commonly the sensitization has an immunological basis and the
symptoms are episodic. Re-exposure to an airborne antigen such as
pollen causes release of histamine from mast cells and basophils,
precipitating immediate bronchioconstriction and labored breathing.
Various drugs are helpful in minimizing the severity of the attacks. Clinical
note: Asthma involves hyperirritability of the respiratory
passages, expressed as contraction of the bronchial smooth muscle,
edema of the mucosa, and increased mucus secretion. It may be
transient, following an upper respiratory tract infection, but more
commonly the sensitization has an immunological basis and the
symptoms are episodic. Re-exposure to an airborne antigen such as
pollen causes release of histamine from mast cells and basophils,
precipitating immediate bronchioconstriction and labored breathing.
Various drugs are helpful in minimizing the severity of the attacks.
Elastic fibers
in the lung. |