|
The adrenal gland consists of
two endocrine tissues, the cortex and medulla, that are functionally
distinct. The glandular epithelia of the adrenal cortex are arranged
in small clusters (zona glomerulosa and reticularis) or cords (zona
fasciculata) with closely associated capillaries. Cells of the
cortex have features common to steroid producing cells, such as
abundant smooth endoplasmic reticulum and lipid droplets, giving the
cytoplasm of these cells a “foamy appearance.” The adrenal medulla
contains clusters of chromaffin cells, a type of neurosecretory
cell, and parasympathetic ganglion cells. The adrenal medulla also
contains a central adrenal medullary vein, a distinctive blood
vessel with longitudinal bundles of smooth muscle in its wall.
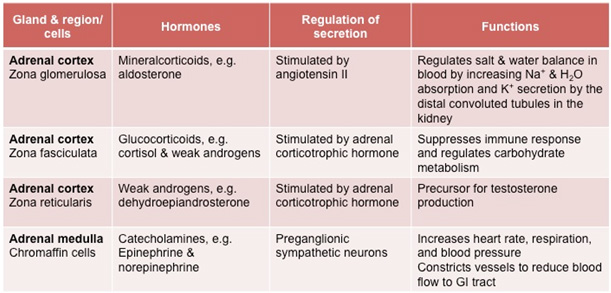
Review the table below describing the features and functions of the
adrenal glands.
- Examine the images below and
these three slides of adrenal gland (sample
1, sample 2
 ,
sample 3 ,
sample 3 ). The
adrenals are flattened glands with concentric layers of
secretory tissue. In the distinct capsule associated with
adipose tissue, notice the small arteries entering the gland and
the vascular plexus just inside the capsule. ). The
adrenals are flattened glands with concentric layers of
secretory tissue. In the distinct capsule associated with
adipose tissue, notice the small arteries entering the gland and
the vascular plexus just inside the capsule.
- On these two slides
(sample 1,
sample 2
 ),
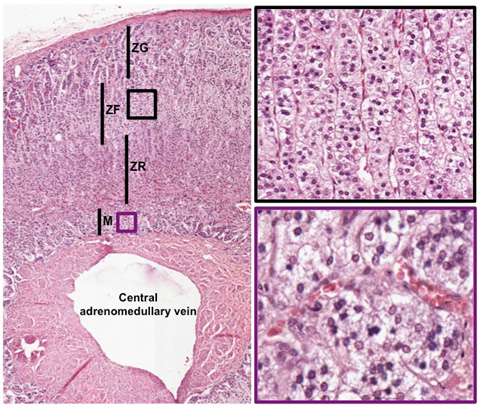
examine the cortex. Identify the three layers or zones in which
the steroid-secreting cells have slightly different
arrangements, with groups of cells separated by fine, well-vascularized
connective tissue septa. The outermost zona glomerulosa has
cells secreting mineralocorticoids arranged in irregular
clusters ("glomeruli"). The middle and widest layer, the zona
fasciculata, has cells secreting glucocorticoids arranged in
strands ("fascicles"). The innermost layer, the zona reticularis,
shows irregular, branching ("reticular") cords of cells
secreting small quantities of weak androgens. ),
examine the cortex. Identify the three layers or zones in which
the steroid-secreting cells have slightly different
arrangements, with groups of cells separated by fine, well-vascularized
connective tissue septa. The outermost zona glomerulosa has
cells secreting mineralocorticoids arranged in irregular
clusters ("glomeruli"). The middle and widest layer, the zona
fasciculata, has cells secreting glucocorticoids arranged in
strands ("fascicles"). The innermost layer, the zona reticularis,
shows irregular, branching ("reticular") cords of cells
secreting small quantities of weak androgens.
- Examine the
medulla, noting the clusters of chromaffin cells, scattered
ganglion cells, and the central adrenomedullary vein.
 Clinical
note: Addison’s disease is an adrenal insufficiency caused by
infection or autoimmune destruction of the adrenal cortex.
Fatigue, low blood pressure, nausea and other symptoms of the
disorder suggest failure of secretion of both glucocorticoids
and mineralocorticoids. Clinical
note: Addison’s disease is an adrenal insufficiency caused by
infection or autoimmune destruction of the adrenal cortex.
Fatigue, low blood pressure, nausea and other symptoms of the
disorder suggest failure of secretion of both glucocorticoids
and mineralocorticoids.
Now try this self-assessment
quiz, no one sees the score but you.
Now for
specialized sensory organs . |