|
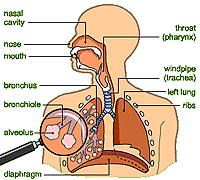 The
main function of the respiratory system is to transfer gases between
the air and blood. The system is comprised of tubes and highly
branched channels, which terminate in dead-end sacs where gas
transfer occurs. Air brought into the body is conditioned and
filtered in the first part of the respiratory system, the conducting
portion (nasal cavity to bronchioles). The second part of the
system, the respiratory portion, consists of the respiratory
bronchioles and alveoli that are involved with gas exchange. The
main function of the respiratory system is to transfer gases between
the air and blood. The system is comprised of tubes and highly
branched channels, which terminate in dead-end sacs where gas
transfer occurs. Air brought into the body is conditioned and
filtered in the first part of the respiratory system, the conducting
portion (nasal cavity to bronchioles). The second part of the
system, the respiratory portion, consists of the respiratory
bronchioles and alveoli that are involved with gas exchange.
The learning objectives for this session are:
- Identify the characteristic
microscopic structural and cellular components of the
respiratory system from the nasal cavity to the alveolus.
- Identify the structural
components of the nasal cavity, including the organization of
the respiratory and olfactory mucosa and explain their function,
respectively, in respiration and in producing the sense of
smell.
- Identify the structural features
of the larynx, comparing and contrasting the true and false
vocal folds.
- Recognize and describe the
structural features and functions of the conducting and
respiratory portions of the respiratory system.
Let's start at the top with
the nasal cavity. |