|
Simple
columnar Simple columnar
epithelia are specialized for absorption. As their name implies,
these cells are taller than they are wide, and their nuclei are
usually located closer to the basal surface.
-
This type of epithelium lines
the gall bladder (H&E
stained sample and a
trichrome stained
sample) and the projecting
villi in the small
intestine.
-
The apical surfaces of the simple
columnar epithelial cells in the small intestine are covered by
microvilli, which provide a larger surface for absorption (seen
below in LM and EM images). Many cells have microvilli at their
apical surfaces, but they are especially well developed in the small
intestine.
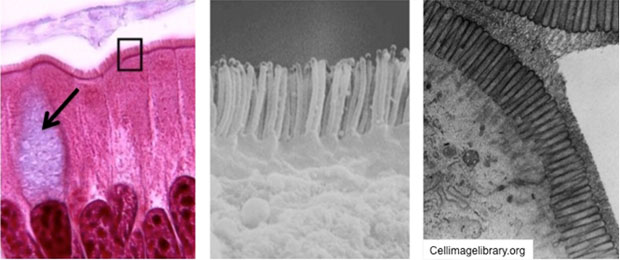
- In this slide, the
glycocalyx
on the microvilli is stained "magenta" by the PAS
reaction, demonstrating the microvilli collectively as the
brush or striated border. The glycocalyx is also visible in
the TEM image of intestinal epithelium seen above in the far
right panel.
- In these two slides of small
bowel, ileum stained
with trichrome and
jejunum stained
with H&E, study the brush border again and examine the
terminal web, the network of actin filaments in the cytoplasm just
below the microvilli.
- Some cells of the simple
columnar epithelium, called goblet cells (arrow in left panel
above), are specialized for secretion of mucus rather than
absorption. Take a look at this
PAS stained slide
to see if you can locate these unicellular goblet shaped glands.
PAS stains the mucin granules that fill the cytoplasm,
demonstrating the overall size and shape of these cells.
Here are some interesting facts about epithelial
cells. |